The Dual Path to Excellence: The Balancing Act of Demystifying CXM and CX Dysfunctions

Most of us know by now that a great Customer Experience (CX) can make or break a business. It’s the secret sauce that keeps customers coming back, spreading the word, and ultimately, driving profits. However, when it comes to enhancing CX, it’s not a one-size-fits-all game. Two key areas are to focus on: Customer Experience Management (CXM) and the direct Customer Experience (CX). In this article, we’ll delve into the differences between addressing CXM dysfunctions and tackling CX dysfunctions.
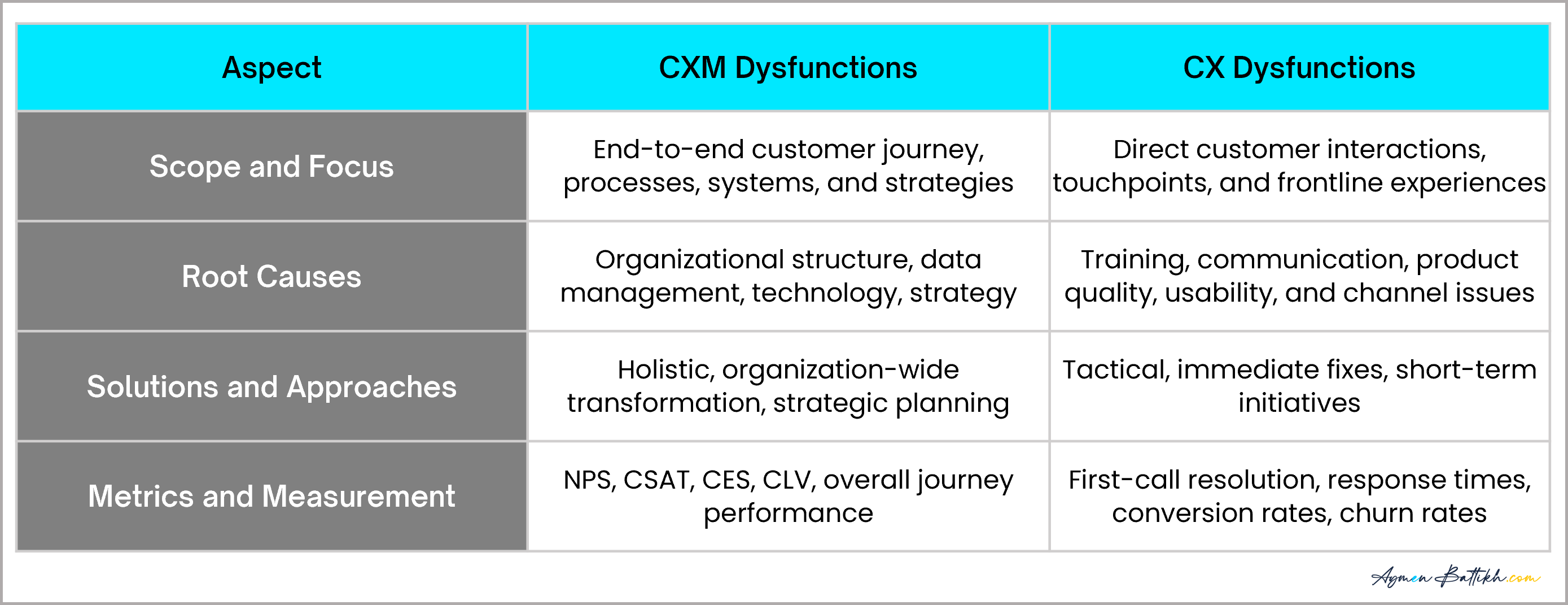
What’s in Scope?
In the quest for customer experience excellence, it’s essential to distinguish between Customer Experience Management (CXM) and Customer Experience (CX), each contributing uniquely to the overall strategy.
CXM represents the broader strategy for managing customer experiences. It involves:
- Mapping cross-channel customer journeys.
- Streamlining back-end processes.
- Implementing supporting technologies.
- Aligning strategies towards a customer-centric experience.
- And, ultimately, aligning customer strategies with the overall organization-centric objectives.
CXM in Practice:
- Apple Inc. sets a benchmark in CXM, ensuring a seamless journey from the retail environment to product unboxing, reflecting a consistent brand experience.
- In sectors like healthcare and manufacturing, CXM dysfunctions, such as poor coordination in patient care or supply chain inefficiencies, can significantly impact the overall experience.
CX narrows down to direct customer interactions and touchpoints, influencing immediate perceptions through:
- Direct service and product experiences.
- Retail, web, and mobile interactions.
- Employee engagement and marketing communications.
- Customer support and feedback mechanisms.
CX Challenges:
- A restaurant struggling with slow service directly affects customer perceptions.
- In banking, the absence of personalized communication can lead to customer dissatisfaction, emphasizing the need for tailored interactions.
Industry Specifics:
- For example, in manufacturing, timely product deliveries and supply chain efficiency directly influence CX, showcasing the critical link between operational efficiency and customer experience management.
- In the automotive industry, integrating online platforms with dealership inventories enhances both CXM and CX by providing a seamless transition from digital to physical interactions.
Key Takeaway
Understanding the nuances between CXM and CX is critical. CXM addresses the holistic orchestration of customer interactions, while CX focuses on the quality of individual touchpoints. Both are crucial and interdependent, necessitating a balanced approach to optimize each aspect for overall customer experience excellence.
Peeling Back the Layers
CXM Dysfunctions
Delving into the depths CXM dysfunctions often stem from fundamental organizational challenges. These include complex issues such as:
- Organizational Structure: Inadequate frameworks that fail to support a customer-focused approach.
- Data Management: Inefficiencies and fragmentation in handling customer data.
- Technology Infrastructure: Outdated or misaligned tech systems that hinder seamless customer interactions.
- Strategic Alignment: Discrepancies between company objectives and customer needs.
Key Contributors to Dysfunction
- Fragmented data silos that obstruct a unified view of the customer.
- A deficit in customer-centric culture, which is essential for driving CX initiatives.
- Misaligned team objectives, leading to conflicting actions and strategies.
- Inefficient processes to capture and act on customer feedback.
For instance, Amazon exemplifies success in CXM by harnessing a data-centric strategy, tailoring the customer journey through insights derived from vast data analytics. In contrast, the automotive industry demonstrates how disconnection between digital services and physical dealership experiences can impair customer satisfaction—a gap that is increasingly being bridged through synchronized digital-physical CXM strategies.
CX Dysfunctions
Identifying and addressing the immediate issues direct CX dysfunctions are more apparent in day-to-day interactions and can be pinpointed to:
- Training Gaps: Customer-facing teams lacking the skills to deliver quality service.
- Inconsistent Communications: Mixed messages that confuse the customer journey.
- Product Issues: Defects or quirks that detract from the customer’s experience.
- Digital Navigation Hurdles: Websites that frustrate rather than facilitate.
- Communication Systems: Platforms that don’t meet the demands of modern customer engagement.
Consider a retailer grappling with pricing discrepancies across channels, leading to customer dismay, as reported in various case studies. In e-commerce, unclear product information is a notorious CX dysfunction, contributing to a spike in return rates.
Bridging the Divide with Strategic Solutions
The interplay between CXM and CX is intricate. A customer-centric culture and streamlined processes are indispensable for mitigating dysfunctions in both domains. By embracing a holistic approach that recognizes the symbiotic relationship between CXM strategies and CX tactics, businesses can achieve a more substantial, lasting impact.
Advanced data analytics and AI play a pivotal role in diagnosing and preemptively resolving potential customer issues, as evidenced by research in predictive customer behavior.
Key Takeaway
Effectively addressing CXM dysfunctions hinges on rectifying core organizational issues and aligning strategies to customer needs, setting the stage for a robust and customer-centric experience framework.
Cracking the Code: Unmasking CXM vs. CX Different Dysfunctions
Crafting a Game Plan
To effectively address both CXM and CX dysfunctions, a dual approach that combines broad organizational transformation with targeted tactical fixes is essential.
Addressing CXM Dysfunctions: Orchestrating the Grand Symphony
- Cultural Transformation: Embedding a customer-centric culture across the organization is pivotal. This includes rallying around customer needs and aligning all business processes to enhance customer experiences.
- Data-Driven Journey Mapping: Utilizing analytics and CRM systems to visualize and optimize end-to-end customer journeys.
- Streamlining Operations: Removing operational friction points by refining processes and leveraging technology.
Examples of Successful CXM Strategies:
- Disney exemplifies CXM excellence by meticulously designing each touchpoint to align with customer expectations, from theme park visits to character interactions.
- In the education sector, aligning student services with academic goals can significantly improve the overall student experience, as seen in various case studies.
Tackling CX Dysfunctions: Fine-Tuning the Details
- Focused Training: Enhancing skills of customer-facing teams to provide quality interactions.
- Rapid Response and Channel Upgrades: Addressing specific customer issues quickly and upgrading communication platforms to streamline customer interactions.
- Product and Service Refinement: Addressing product defects and functionality issues for a smoother customer experience.
Examples of Targeted CX Solutions:
- An e-commerce website may invest in personalized recommendations and website optimization to enhance the shopping experience.
- A telecommunications company can focus on reducing service wait times as a key area of improvement.
Forging CXM and CX Synergies for Sustainable Success
- Integrating CXM and CX initiatives leads to a more impactful customer experience strategy.
- Leveraging strengths across CXM (like data unification and omnichannel consistency) and CX (like improved agent training and tools) drives greater combined results, enhancing both the holistic journey and individual touchpoints.
Key Takeaway
A balanced approach, where organizational changes in CXM complement tactical enhancements in CX, ensures a comprehensive and effective customer experience strategy. This integrated method not only addresses immediate issues but also sets a foundation for long-term customer relationship management.
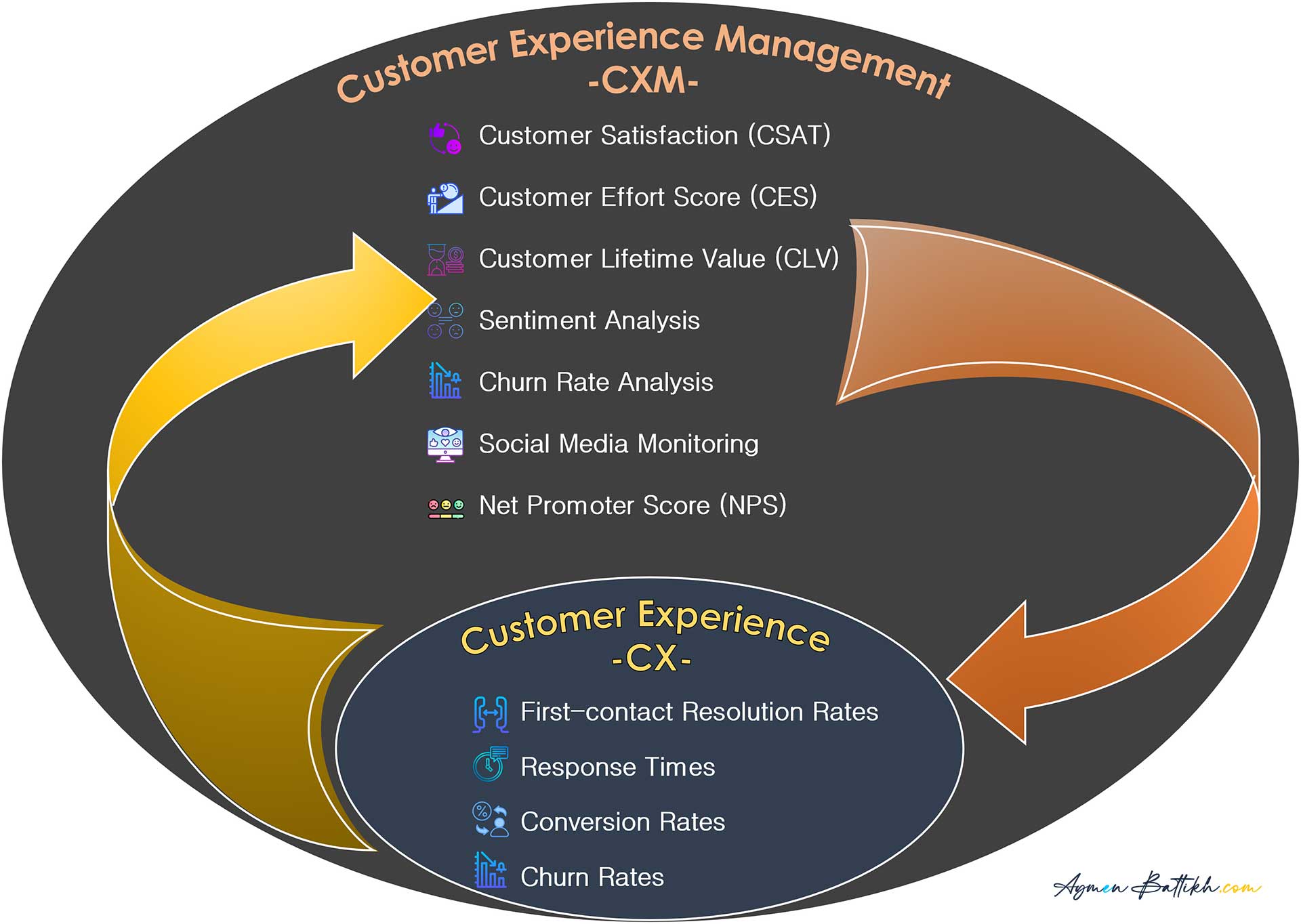
Scematization of the Relationship and Interdependency of CXM and CX Metrics
Tracking Progress and Measuring Success
Understanding and improving customer experiences hinge on effectively measuring both CXM and CX. It necessitates a balanced use of traditional metrics and the integration of emerging, data-driven insights.
Key CXM Metrics: Strategic Alignment and Impact
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT): Reflects the effectiveness of customer-centric strategies in service quality.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): Indicates the success of aligning customer journeys with organizational goals.
- Customer Effort Score (CES): Measures the impact of streamlined operations and system integrations.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): Gauges brand loyalty and the overarching success of CXM strategies.
Evolving Beyond Traditional Metrics
While traditional CXM metrics like NPS and CSAT remain relevant, sole reliance on such surveys has limitations. They can be complemented with advanced analytics that can provide deeper, forward-looking customer insights:
- Churn Rate Analysis: Links operational efficiency with customer retention.
- Sentiment Analysis and Social Media Monitoring: Offer real-time feedback on customer perceptions, influenced by CX initiatives.
- AI-Enabled Voice-of-Customer Analysis: Bridges customer feedback with actionable insights, vital for CXM improvements.
CX Metrics: Tactical Execution and Immediate Feedback
- First Contact Resolution Rates: Indicate the effectiveness of customer service training and response strategies.
- Average Handle Time: Reflects operational efficiency in customer interactions.
- Conversion Rates: Show the impact of direct customer engagement strategies.
- Churn Rates: Provide immediate insights into the effectiveness of CX tactics in retaining customers.
Interconnected Impacts and Synergies
The interconnected nature of these metrics underscores the symbiotic relationship between CXM and CX. For instance, improved first contact resolution rates (CX) can enhance customer effort scores (CXM), showing how tactical CX enhancements bolster broader CXM goals. Increased CSAT scores can positively influence CLV, demonstrating the long-term benefits of strategic CXM initiatives.
CX Theory and Tailored Practices
Extensive research in areas like the Journal of Service Theory and Practice highlights the importance of experiential components in customer satisfaction. Tailored solutions, such as leveraging AI for personalized e-commerce experiences or bridging digital and physical touchpoints in the automotive sector, are crucial for addressing specific industry needs.
Key Takeaway
A comprehensive set of metrics, combining traditional approaches with innovative analytics, equips businesses with a nuanced understanding of their impact on customer experiences. This holistic approach is key to continuously refining strategies and achieving excellence in both CXM and CX domains.
Moving Forward: Charting the Path to Excellence
In customer experience, the journey toward excellence demands a nuanced and multifaceted strategy that seamlessly integrates CXM and CX.
Embracing Interdependencies for Holistic Growth
The interplay between CXM’s strategic scope and CX’s tactical depth is not just complementary but essential. Upgrading technological infrastructure for data unification, a CXM endeavor, paves the way for personalized customer interactions, a core CX goal. Similarly, enhancing frontline empathy and skills, a focus in CX, enriches the broader journey insights crucial to CXM. Recognizing and leveraging these interdependencies is key to building a robust customer experience framework.
Analytical Insights Paired with Tactical Execution
While analytics, including AI-driven sentiment analysis, offer invaluable foresight into customer preferences and behaviors, they are most effective when paired with actionable strategies. This means translating data insights into concrete improvements in both the overarching journey (CXM) and specific touchpoints (CX). The goal is to ensure that analytical depth informs and enhances operational agility.
Customer-Centricity: A Continual Dialogue
Staying ahead in the CX game requires an unwavering commitment to understanding and evolving with customer needs. This goes beyond internal metrics to engaging in ongoing dialogues with customers. These co-creating solutions resonate with their evolving expectations. It’s about maintaining an ‘outside-in’ perspective, where customer insights shape strategic decisions.
Starting Small, Scaling for Impact
Embarking on CX transformation need not be overwhelming. Initiatives like cross-functional customer journey mapping and leveraging real-time customer feedback systems can yield immediate, actionable insights. These small but significant steps, supported by the latest digital experience technologies, set the stage for broader, scalable impacts.
Commitment to Continuous Learning and Adaptation
The landscape of customer experience is ever-evolving. Embracing a growth mindset, where continuous learning and adaptation are integral, propels organizations forward. Decisive actions, even incremental, lay the groundwork for uncovering future opportunities. Nurturing this mindset ensures that CX excellence is not a destination but a continuous journey, adapting to the changing tides of customer needs and market dynamics.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, mastering CXM and CX is an ongoing process of strategic alignment, tactical refinement, and relentless customer-centricity. By integrating these elements, businesses can address current challenges and pave the way for enduring success in a world where customer experience is paramount.
Let's Chat!
Tell me how I can help you?
Got questions or ideas? Want a free consult? I’m just a click away. Reach out and let’s kickstart your success journey!